Good Day!!
Be sure to date your notes each day and write in your planner
- Review Scientific Principles (listed below)
- Reading 7.3
- Are you able to answer your driving questions? — Let’s consider:
1) What makes one color different from another
2) Mixing colors –Activity 9.2 on Computers
3) Infrared Light and the remote (Homework 12.1 in class)
- In Class: Activity 12.2
Final assignment: Due —
Red –Nov. 30th White— December 1st
Write a paper (one page) using scientific principals and terms that (You may include a diagram of the eye and why light is different colors to our eyes from class evidence to write your reasoning about light and its properties.
Include the experiences you had in class for evidence whether or not we can believe our eyes. Use your notes and reading answers to help you. Ask me about this when you come to class.
Let me know if you think your paper will be more that three pages.
Test : November 14th and 15th
- Scientific Principles (below)
- Scientific Method–Using Hypothesis, Data , and Reasoning from labs
- Class Roles
- Relevant terms —
Relevant terms from class:
Reasoning clear path of view how light travels wavelength cone refraction eyes neurons speed of light ROYGBIV shadow lens brain object retina photoreceptor electromagnetic spectrum Speed of Light contrast shadow pupil rod reflection light Infrared UV diffraction
Scientific Principals:
- An object can be seen if four conditions are met: there is an object, an eye, a source of light, and a direct path between the object and the eye.
- Light must enter the eye or sensor to be seen or detected.
- The brighter an object appears, the more light that reaches the eye or detector from it.
- Light travels in straight lines.
- Light continues traveling until it reaches an object that scatters or absorbs it.
- A shadow is formed behind an object that blocks the path of light.
- A shadow is seen by detecting that less light reaches the eyes from it than from the area surrounding it.
- Scattering occurs when light bounces off an object in all directions. This occurs when the surface of the object is rough and unpolished.
- Reflection occurs when light bounces off an object only in a certain direction. This occurs when the surface of the object is smooth and polished.
- A reflection of one object is seen in a second object only if the second object reflects light, not if it scatters it.
- Some objects are transparent and let light pass through them.
- When light reaches an object, it is scattered (or reflected), transmitted, absorbed, or some combination of these.
- Light can make things happen when it is absorbed.
- When different colored lights are mixed, they appear as a new color, brighter than the original colors.
- White light is a mixture of all colors of light—it is the brightest color. Black is the color associated with the absence of light.
- Filters color light by absorbing certain colors and transmitting the rest.
- Colored objects scatter only certain colors of light and absorb the rest.
- There are many different wavelengths of light. Most of these cannot be seen.
- Different wavelengths of visible light appear to us as different colors.
November 2, 2016
We will use the following with our problem solving focus:
Student’s Science Project Finds Toilet Water Cleaner Than Restaurant Ice.
A seventh-grade student in Florida was awarded first place for her science fair project that found some toilet water is cleaner than ice served at area restaurants, according to a Local 6 News report.
Student Jasmine Roberts checked five fast-food restaurants near the University of South Florida and found there was more bacteria in the ice people were drinking than there was in the same restaurants’ toilet water.
“When I get ice, sometimes I order ice just to chew on it, and now I know I’m not going to do that anymore just because of the amount of bacteria I found,” Roberts said.
Since the Benito Middle School student completed the project, she has received international attention.
Dr. Daniel Lim, who is a microbiology professor at USF, said he was not surprised the toilet water had less bacteria than restaurant ice.
If you don’t clean the receptacle, the materials routinely, there may be a possibility of biofilm or residual material remaining in that receptacle,” Lim said.
Jim Griffith, the president of Suncoast Ice Machines, sells, leases and services ice machines. He also wondered about the cleanliness of the ice dispensers the students sampled.
The Florida Department of Business and Professional Regulation checks ice machines during restaurant inspections twice a year.
Roberts won $800 for the project.
Let’s use Jasmine’s experiment as an example for our problem solving focus:
“My hypothesis was that the fast food restaurants’ ice would contain more bacteria that the fast food restaurants’ toilet water.”
After testing water from the toilets and ice taken from 5 area fast food restaurants, her conclusion:
“I found that 70-percent of the time, the ice from the fast food restaurant’s contain more bacteria than the fast food restaurant’s toilet water.”
4 Parts of a Scientific Experiment: (Textbook pages 754 & 755)
- Independent Variable—What is measured; the manipulated variable
- Dependent Variable —Results, data
- Constant——————Conditions of the experiment that do not change
- Control——————-Used for comparison to independent variable
Placebo—-a fake independent variable to understand the effect of just using the independent variable
- Retinal fatique: We will use the blank sheets and those with green , blue, and red dots to explore —Make a data table :
| Color eyed for 30 seconds | Reaction | Observation |
| Red | ||
| Blue | ||
| Green |
- Comics and dissecting scopes or magnifying lenses.
| light | clear path of view | how light travels | wavelength | cone | refraction |
| eyes | neurons | speed of light | ROYGBIV | shadow | lens |
| brain | object | retina | photoreceptor | electromagnetic spectrum | |
| contrast | shadow | pupil | rod | reflection |
October 26th, 2016
Write your driving question in your notes and textbook.
Making Sense (Reasoning Assignments checked for completion)
List in class: what you think is needed to see an object.
Assignment: Draw a model of how light travels from a light bulb. Due 10/28/16
 Ellen Ochoa |
- Luis Walter Alvarez, Nobel Prize-winning physicist
- Franklin Chang-Dìaz, astronaut
- Mario Molina, Nobel Prize-winning chemist
- Carlos Noriega, astronaut
- Ellen Ochoa, astronaut
- Severo Ochoa, Nobel Prize-winning biochemist
October 13 – 26th
Article assignment: Please click on the following link —
PROGRESS GRADE ADJUSTMENTS AND ASSIGNMENT REVISIONS BEING MADE (10/18 – 10/26)
Cornell Notes for Science:
Cornell Notes distributed for use in class and will be available each class.
|
||||||||||||||||
September 30, 2016 Red Day
- Get a computer . Open two tabs:
- Google classroom —Let’s do the quiz
- your textbook.
- Turn in your Learning Style and Intelligence Strengths graphic
- Hanger Lab>>>>>>>>>>>>> Please Read
- Uncontrollable Foot>>> Wait for instructions
*********************************
Take out a blank sheet of paper and write your heading:
Name (first and last) Period/Day
Subject:
Date
Please wait quietly. Thank you 🙂
September 29, 2016—-White Day
September 28, 2016 —Red Day
Textbook: http://eugene4j.iqwst.com/webapp
Class site: https://blogs.4j.lane.edu/mellyhollowayrooscience
or: http://tinyurl.com/zq6q4gb
Planner: Connect to your
- editable textbook —post your observation of the candles and sketch
- Google Classroom
🙂 Please notice that there are now bins for storage to be used during class. After you have your notes and planner ready to use, place jackets, other books and anything else you have with you in the section closest to you.
September 27:
Assignment:
I. Complete a copy of your Learning Styles and Intelligence Strengths to be placed in your folder while in class.
II. Use your provided log in (username and password) while and class and at outside of class to access your digital editable textbook at :
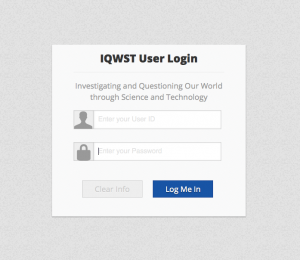
I. Be sure to open you textbook and add your First entry: Scientific Method Practice. In the body of the message include:
Claim–Problem, Materials, Procedure
Evidence–Write and Do an Experiment–
- Make a data table and record data
Reasoning—Think about and analyze
- Communicate Results
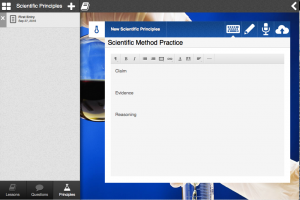
II. Make a drawing of what you saw in class using the “paint brush option”
Save both each time by selecting the cloud with the arrow in the upper right corner.
______________
In addition to the Safety Rules in your notes you copied in class :
- Leave the lab area and equipment in the proper place at the end of lab.
- Wash your hands before leaving the lab.
- Return lab material to proper places after use
- Wash used glassware and instruments
- Wipe off work areas
- Clean the sink after use
September 23: ****Safety Quiz next week***
Reflection 1:
Go to your google classroom, and find the assignment (Reflection 1) click on create and work in your Google Docs to privately submit .
Lab Safety: Make sure that the lab is safe
Necessary steps to end labs:
- Leave the lab area and equipment clean
- Wash your hands–a)Palm to Palm b) Interlaced c)Thumbs d) Rotate hands with soap before rinsing
- Return Lab materials and equipment to proper places after use.
- Wash used glassware and instruments with cleaning powder and rinse them in clear water.
- Wipe off work areas as directed
- Clean sink
- Never leave an experiment
Remember: We share the lab space and clean up before leaving
September 22
Thinking —Brains on —Ask questions —-Time use
Technology —Tools
Teamwork —Contribute to the learning environment
I. Solve the problems you copied into your notes while in class. Show your thinking.
II. Brain Teasers:
1- 20
September 19, 2016
Its Flu Season and we are starting the school with safety:
Focus on Safety (For periods 2, 3,& 4):
Please have students:
- Use glue sticks to attach the handout to a page in their notes
- View
- Safe coughing, sneezing video:
- How to Cough and Sneeze Hygiencally: http://pisdtv.pisd.edu/instructional-technology/features/O_iad_w93ed1UzUxwjwT
b . Mythbuster videos:
- The Safe Sneeze
- Bathroom Hygiene : https://www.youtube.com/watch?v=1pFww_EaLiY
- Have students Copy (in their science notes after the page they glued their “Safety Rules”& Check off terms heard in class:
- Identify a problem
- Analyze and Write Conclusions
- Form a Hypothesis
- Communicate Results
- Collect Data
- Perform an Experiment
- Record Data
Tell students that not only is it flu season, but we share space, and in a science class we need to approach this hygienically;
- It is estimated that washing hands with soap and water could reduce diarrheal disease-associated deaths by up to 50% 1.
- that 80% of infections are spread, Handwashing can reduce the risk of respiratory infections by 16% 4.
- More than 50% of healthy persons have Staphylococcus aureus living in or on their nasal passages, throats, hair, or skin 6.
Asked why may it is appropriate address this in a science class.
For period 5 (Advanced Topics) —-
- World Health Organization. Water for health: taking charge. 2001.[PDF – 6 pages].
- Rabie T, Curtis V. Handwashing and risk of respiratory infections: a quantitative systematic review. Trop Med Int Health. 2006;11(3):258-67.
- Food and Drug Administration. Bad Bug Book – Staphylococcus aureus.
Scientific Method Name ____________
Science Safety Rules Period __
The Bikini Bottom gang has been learning safety rules during science class. Read the paragraphs below to find the broken safety rules and underline each one. How many can you find?
SpongeBob, Patrick, and Gary were thrilled when Mr. Krabbs gave their teacher a chemistry set! Mr. Krabbs warned them to be careful and reminded them to follow the safety rules they had learned in science class. The teacher passed out the materials and provided each person with an experiment book.
SpongeBob and Gary flipped through the book and decided to test the properties of a mystery substance. Since the teacher did not tell them to wear the safety goggles, they left them on the table. SpongeBob lit the Bunsen burner and then reached across the flame to get a test tube from Gary. In the process, he knocked over a bottle of the mystery substance and a little bit splashed on Gary. SpongeBob poured some of the substance into a test tube and began to heat it. When it started to bubble he looked into the test tube to see what was happening and pointed it towards Gary so he could see. Gary thought it smelled weird so he took a deep whiff of it. He didn’t think it smelled poisonous and tasted a little bit of the substance. They were worried about running out of time, so they left the test tube and materials on the table and moved to a different station to try another experiment.
Patrick didn’t want to waste any time reading the directions, so he put on some safety goggles and picked a couple different substances. He tested them with vinegar (a weak acid) to see what would happen even though he didn’t have permission to experiment on his own. He noticed that one of the substances did not do anything, but the other one fizzed. He also mixed two substances together to see what would happen, but didn’t notice anything. He saw SpongeBob and Gary heating something in a test tube and decided to do that test. He ran over to that station and knocked over a couple bottles that SpongeBob had left open. After cleaning up the spills, he read the directions and found the materials he needed. The only test tube he could find had a small crack in it, but he decided to use it anyway. He lit the Bunsen burner and used tongs to hold the test tube over the flame. He forgot to move his notebook away from the flame and almost caught it on fire.
Before they could do another experiment, the bell rang and they rushed to put everything away. Since they didn’t have much time, Patrick didn’t clean out his test tube before putting it in the cabinet. SpongeBob noticed that he had a small cut on his finger, but decided he didn’t have time to tell the teacher about it. Since they were late, they skipped washing their hands and hurried to the next class.
Thanks to: Worksheet created by T. Trimpe 2003 http://sciencespot.net/
Safety focus:
How to cough and sneeze hygiencally
http://pisdtv.pisd.edu/instructional-technology/features/O_iad_w93ed1UzUxwjwT And Mythbuster’s The Safe Sneeze—https://www.youtube.com/watch?v=3vw0hIs2LEg
Bathroom Hygiene: https://www.youtube.com/watch?v=1pFww_EaLiY
Washing Hands: About 20
- Palm to Palm
- Interlaced fingers
- Rubbing Thumbs
- Rotate hand over hand
- World Health Organization. Water for health: taking charge. 2001.[PDF – 6 pages].
- Rabie T, Curtis V. Handwashing and risk of respiratory infections: a quantitative systematic review. Trop Med Int Health. 2006;11(3):258-67.
- Food and Drug Administration. Bad Bug Book – Staphylococcus aureus.
Team roles:
- Resource Manager
- Task Manager
- Recorder/Reporter
- Reader
Period 5 : Advanced Topics: Nautilus Live
Sept. 8, 9 2016
COPY notes……
- School Photos ???
- Folder—Goals, Health Info
- Learning Style—How do I learn?
Number a paper from 1 – 20.Place in folder. http://www.educationplanner.org/students/self-assessments/learning-styles-quiz.shtml
- Class Procedures:
- Entering class
- Walking in halls
- Get to work immediately
- End of period dismissal
- Coming to attention
- Keeping your notebook
- Working in groups
- Let’s get thinking—Brain Teasers!
- READ the handout
September
First full week:
GOOD DAY!!!!!
VI.Books distributed:
In Science Notes : Number a page from 1 – 10
Select at least 10 pg.#s that make you think: Wow!, Yuck!, What?, or Huh?
Write what questions come to mind
VII. Learning Style
- Get a computer
- Let’s confirm your email and Google Docs use: The signed sheets you turned in (sent home before school started) activates your technology use. 🙂
- Google: Learning style Inventory: Click on and use the Education Planner 20 questions site to take the inventory—–draw the resulting bar graph in your notes:
Learning style results:
V A T
- Google >>>>>>>Edutopia Multiple Intelligences –self assessment —http://www.edutopia.org/multiple-intelligences-assessment Answer the series of questions. List the resulting intellegences with your percentages:
Verbal-Linguistic————–%
Logical-Mathematical——–
Spatial————————
Bodily-Kinesthetic——
Muscial——————-
Interpersonal————-
Intrapersonal—————
Naturalist——————-
Save
Save
function googleTranslateElementInit() {
new google.translate.TranslateElement({pageLanguage: ‘en’, layout: google.translate.TranslateElement.InlineLayout.HORIZONTAL}, ‘google_translate_element’);
}
Save
Save
Save
Save
Save

No comments